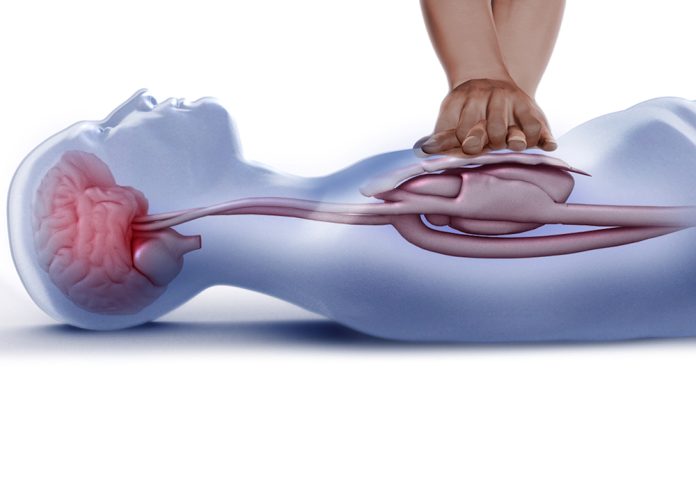
Chest compressions are essential, but we also need to know how deep chest compressions should be. We also need to recognize what kind of chest compression to do—medical examinations on people who have suffered a heart attack. Based on the variation, they had at least 5 centimeters of rescue breathing depth, leading to better rehabilitation. And better survivorship percentage and neurologic consequences. Yet, there was a greater chance of untreatable injury when the pressure depth was 6 cm or more. visit here
It means that the compression depth assists in the 2015 American Medical Association. And International Healthcare Improvement recommendations for independent people. CPR should be at least 5 centimeters (2 inches) and far less than centimeters (about 2 inches) (2.5 inches).
Table of Contents
How can you tell if your chest compressions are at the correct level
In a broad sense, it’s more vital to have too much pressure than not enough. People who don’t do enough chest compressions may have fractured bones and internal bleeding. People who don’t do enough chest compressions would almost surely die. Broken bones aren’t suitable, but death is worse for sick people.

Exercise is the single most effective way to understand how much pressure they will be under when they give a speech. But if you don’t work in a clinical area, that can be hard to have that profession in. The level of force needed to squeeze blood into the whole body is more than most individuals consider. CPR should be forceful, with rescuers trying to push faster and faster with two hands. Health doctors usually don’t do CPR alone for more than two minutes, so they don’t get tired.
The number of compressions to be delivered per minute
Push very tough, and: 100 to 120 compressions a minute is good. As long as you haven’t been taught how to do CPR, keep doing chest compressions till children progress. Or until an urgent situation medical workers take over, then you can stop. If you know how to do CPR, you should open the air passages and generally breathe for those who aren’t living.
Recommended depth for compressing the chest of a newborn baby
A depth of one-third to one-half of an innocent child for chest compressions. Or the child’s posterolateral chest surface area recommended BLS CPR Certification Charlotte.
Depth and percentage of chest compressions current boundaries for adults
Chest compression is a tiny percentage of more than 80%. There is a compression percentage of 100 to 120 per minute. People should have at least a compression depth with at least 50 mm (2 inches) in adults and at least 1/3 of the AP aspect of their chests in premature infants.
CPR in 4 steps
Let’s check out 4 easy steps of CPR to understand how deep chest compressions should be more clear.
Step 1: Shake and shout
You also should confirm the threat and take a glance at the consequences before you try to help somebody unaware. Those with a panic attack will just not be exhaling, or they won’t be getting enough oxygen. People also won’t know.
Shake the patient’s shoulders and start questioning them if they’re okay. If everyone is adjacent, inquire people to remain because you’ll need them. People will notice you even if you’re alone.
Step 2: Cover mouth and nose with a cloth.
- Putting a handkerchief or change of clothes over the mouth and nose could help stop an infectious disease. Wouldn’t stick your hand near your own.
- Whether you’re confident, that is getting enough oxygen, and after that, throw them in a safe location and help them get better.
Step 3: Give chest compressions.
Do not offer cardiopulmonary resuscitation at this point in the game.
- The individual should take a knee beside you.
- Heel with their chest, including one hand. Locate your second hand up of this one. It’s time to make a fist.
- As you keep your hands simple, use the heel of your hand to force the breastbone down. And because then the chest is pushed down among 5–6 centimeters. Then you can let go of it.
- Do that at a percentage of 100 to 120 chest compressions per minute. It’s about two minimizing per moment, so do it.
Step 4: Keep going
- It’s vital to maintain continuity until psychiatric counseling comes to take around. Or the individual begins to show indications of waking up. It could be wheezing, turning their attention, talking, or getting enough oxygen.
- If you’re exhausted when someone near the area can assist, tell them to keep going.
CPR Studies Judgement
Given that juvenile CPR studies in the same way that adults can. Most information for chest compression length. Included in these recommendations are based on professional judgment. And data from physical results taken from chest CT. For kids, chest compression administers up to 1/2 the iPad of the chest. As per professional opinion before 2010, regulations publish. So, two studies, including children’s exact bodies with chest CT., both of which were done in 2009, discovered that half of the iPad was too excessive.

When used as the chest compression length for kids. The American Medical Association and International Healthcare Improvement recommendations. For adolescents, CPR recommends chest compression depths of at least one-third the average pressure of the chest. And around 5 cm for all kids aged one and at the beginning of adolescence throughout 2010.
One epidemiological survey of physician CPR demonstrates. That chest compression intensity is higher than 5 cm. It connects with an increase in quality in short-term consequences. Yet, kids under the age of eight years were 8 (10 percent) amongst respondents of this study. Thus, this research may not get enough knowledge for smaller kids. Must pay close attention to the constant evolution of the body frame. Since the young adolescent newborn is in the early stages of development, older kids and small kids may have vast variations in bone structure. And hence recent regulations of chest compression may be too extensive for smaller kids.
Use chest CT to see if the recent regulations concerning chest compression complexity are good enough for kids of all ages. If they are, they change to make them more specific for kids of all ages.
When to use CPR and when not to
Whenever an adult can’t breathe at all, use Resuscitation. Use CPR for a kid or a newborn if they’re not inhaling and you need to help them. Suppose the immediate family members don’t respond. Because they only use Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation. Once you speak with them or swipe them.
If someone isn’t getting enough oxygen, give Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation. It can ensure that oxygen-rich blood vessels dilate to the brain even if they don’t. If someone doesn’t get enough oxygen, they can have neurological damage or die in less than 8 minutes.
If an individual stops inhaling in any accompanying direction. They may need some cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
- a cardiac event or cardiovascular system failure
- Strangling
- a car crash on the road
- There was a close call with drowning.
- strangulation
- contaminating
- There was too much drug or alcohol for the body to handle.
- a person who inhaled smoke
- Faulty electrical equipment
- Its unexpected child death symptoms might have caused this.
Unless the individual is getting enough oxygen, don’t do CPR. Kids only do it when they aren’t inhaling and their plasma isn’t moving. People should ensure that the client doesn’t react to call to awareness before they begin CPR.
FAQ’s How deep should chest compressions be
- What are the 2015 CPR guidelines for people who aren’t trained?
Good Samaritans should call 911 before they try to help someone hurt. Inexperienced good Samaritans should undertake CPR, which is still an excellent way to save lifestyles from heart failure. Suppose someone is receiving training in CPR and can do deep breathing. The new regulations state that if they can. They should add breathing to a cycle of 30 contractions. And relaxation and two exhalations.
- What is the “Systems of Care” section in the latest edition?
This suggestion highlights that everybody has a part to play in saving lives after a heart attack. The guidance involves taking steps to allow organizations. It creates a treatment system that everyone can use.
3. How long has CPR been documented?
When you congratulate a person who secured your daily life, it’s the best thing you can do. It is thought that a person from Minnesota with a history of CPR continued existence. When did it take? It took 96 minutes to finish.
4. Is it possible to die in the event of a code blue?
Code Blue is a way to say that someone is dead. Unless someone in the doctor’s office has a chest that doesn’t work, this word means it. Also, with ideal CPR, in-hospital medical emergencies have a fatality rate of about 85%.
5. Why aren’t you able to administer CPR when lying in bed?
The intensity of chest compressions is essential because external chest compressions aren’t inclined to work. To get the correct depth of chest compressions, you need to put the person on a strict, horizontal plane. A pillow at home isn’t likely tough enough to use good chest compressions.
Summary of how deep should chest compressions be
CPR is a life-saving first aid method. It can make a big difference if someone has a cardiac arrest or stops the respiratory system after a disaster or injury.
If the individual is a kid, there are many stages. Yet, the fundamental process of chest compressions. And life-saving inhales will stay the same, even though there will be new ways to do them. Always use CPR whenever an individual has gone unconscious, not when still alive. To start CPR, you should check the individual to see if they react to sexual or nonverbal commands. We hope you got How deep should chest compressions be.