Table of Contents
Abdominal Cavity Definition
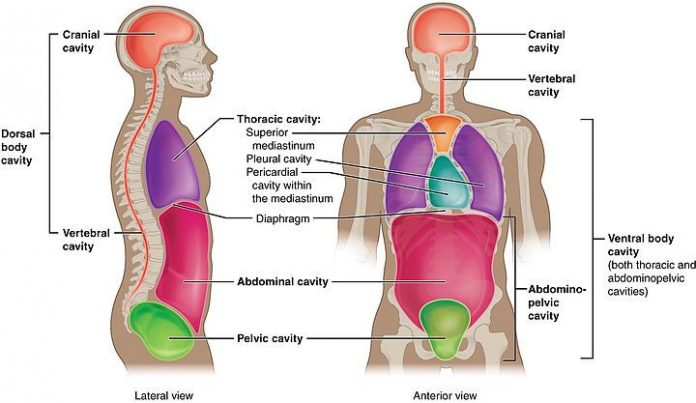
The cavum may be a giant abdominal cavity found within the body of mammals between the chest cavity. It’s separated from the pectoral diaphragm and therefore the cavity. A protecting layer that’s referred to as the serosa, that plays a job in immunity, supporting organs, and fat storage lines the cavum. As shown within the below diagram on the left, the cavum has been divided into 9 completely different areas, wherever each organ doesn’t essentially solely occupy one. This division helps with the diagnosis of diseases that supported the place wherever an individual is experiencing abdominal pain.
1.0Abdominal Cavity Organs
Our abdomen contains organic process, procreative, and excretion organs. You’ll notice a number of them within the following diagram. Detain mind that the body part is taken into account as a part of the cavity.
1.1Stomach
A thick-walled organic process organ found on the left facet of the abdomen that’s divided into four regions: the portal, fundus, body, and orifice. It’s continuous with the esophagus on top of it that carries food from the mouth and passes through the diaphragm and into the abdomen, and is followed by the primary portion of the tiny gut, referred to as the small intestine. The abdomen is that the second web site of digestion in humans when the mouth and it serves to maneuver food around among itself, combine it with stomachic juices, and begins the digestion of proteins.
1.2Liver
This is the most important organ within the abdomen. it’s found on the higher right facet of it, right underneath the diaphragm. it’s 2 lobes that are separated by a ligament. The liver plays an important role in our bodies because it maintains traditional glucose levels, produces digestive juice, and detoxifies the blood.
1.3Gall Bladder
The gall bladder is found below the liver and is connected to that. It stores and concentrates digestive juice that’s then sent to the small intestine once required for fat digestion and absorption.
1.4Spleen
The spleen is a component of the system. Its functions embrace collaborating within the production of white blood cells, storing platelets, and destroying dead red blood cells and harmful substances.
2.1 Introduction
The cavity may be a bowl-like structure that sits below the cavum. Actuality pelvis, or lesser pelvis, lies below the girdle brim. This landmark begins at the extent of the sacral elevation posterior and therefore the os syphilis interiorly. The house below contains the bladder, rectum, and a part of the colon. In females, the pelvis conjointly homes the female internal reproductive organ, fallopian tubes, and ovaries. Data of anatomy distinctive to females is crucial for all clinicians, particularly those within the field of topology and gynecology.
Go to:
2.2Structure and performance
The female internal reproductive organ sits within the center of the feminine cavity (Figure two.) the foremost common position of the female internal reproductive organ within the cavity is anteverted and ante flexed.
[1] “Version” refers to the angle between the cervix and therefore the duct. AN anteverted female internal reproductive organ seems “tipped forward” within the cavity. An extroverted female internal reproductive organ is “tipped backward.” Retroversion may be a traditional variant however will result in dyspareunia. Also, retroversion of a big female internal reproductive organ correlates with higher rates of duct injury and stillbirth.
[2]”Flexion” is the term for the angle between the cervix and the female internal reproductive organ body. Ante flexed means that the female internal reproductive organ is bent forward. Retroflex means that the female internal reproductive organ bends backward. Sometimes, retroflection is seen when abdominal delivery and will result in the connective tissue that attaches the female internal reproductive organ body to the wall, inflicting the complex body part to bend posteriorly.
[3] But, the info supporting this theory is restricted.
2.3Embryology
The organs of the feminine procreative tract every has a novel embryological origin. The precise embryonic timeline during which these organs develop continues to be a hospitable dialogue as a result of most embryologic studies use animal models with completely different physiological conditions ages. However, there’s an agreement that the ovaries are the primary to develop. They arise from the surface of the mesonephros at the endocrine gland ridge.[5] Later in development, the ovaries descend into the pelvis with steering from the gubernaculums. The inferior facet of the gubernaculums afterward becomes the spherical ligament of the female internal reproductive organ and terminates at the labium
2.4Blood provide and Lymphatic’s
Arterial
The anterior branch of the inner arterial iliac provides most of the feminine procreative organs. The arterial provides the bulk of the female internal reproductive organ. the lower female internal reproductive organ phase encompasses twin blood provide that has branches of the arterial. The ovaries are AN exception as a result of they receive blood from the gonad arteries that descend from the aorta.
Venous
The blood vessel provides of girdle organs follows the blood vessel supply. The venous blood vessel receives blood from the female internal reproductive organ and drains into the inner vena. The gonad veins receive blood from the ovaries. the proper vein drains its contents directly into the inferior venous blood vessel, whereas the left vein drain is into the left vena renal is. The accrued length of the left vein makes it additional vulnerable to compression, particularly throughout gestation.[7] vein compression will result in girdle blood vessel compression syndrome. The ensuing girdle vasculature congestion may be a reason for chronic pelvic pain and will occur in non-pregnant patients moreover
Lymphatics
The liquid matter network of the pelvis is advanced but is crucial to grasp once staging and treating medicine malignancies. Generally, the girdle organs drain into the inner and external os humor nodes
2.5Muscles
The inferior border of the cavity is that the girdle diaphragm. It’s created from a gaggle of muscles. From posterior to anterior, these muscles include:
- Performs
• Coccyges
• Iliococcygeus
• Pubococcygeus
• Puborectalis
-
Cavum,
The largest hole of the body. Vertically it’s surrounded by the rachis and therefore the abdominal and alternative muscles. The cavum contains the larger part of the canal, the liver and duct gland, the spleen, the kidneys, and therefore the adrenal glands set on top of the kidneys.
The cavum is lined by the serosa, a membrane that covers not solely the within a wall of the cavity (parietal peritoneum) however conjointly each organ or structure contained in it (visceral peritoneum). The house between the visceral and membrane bone serosa, the cavity, usually contains a tiny low quantity of bodily fluid that allows free movement of the internal organ, significantly of the epithelial duct, within the cavity. The serosa, by connecting the visceral with the membrane bone parts, assists within the support and fixation of the abdominal organs. The varied attachments of the serosa divide the cavum into many compartments.
Some of the internal organs are connected to the abdominal walls by broad areas of the serosa, as is that the duct gland. Others, admire the liver, are connected by folds of the serosa and ligaments, and typically poorly equipped by blood vessels.
The lomenta are folds of serosa introduction nerves, blood vessels, humor channels, and fatty and animal tissue. There are 2 lomenta: the caulk hangs down from the colon of the big gut like an apron; the momentum is way smaller and extends between the abdomen and therefore the liver.
-
Abdomen
The muscles of the abdomen defend very important organs beneath and supply structure for the spine. These muscles facilitate the body to bend at the waist. The foremost muscles of the abdomen embrace the muscles abdominals ahead, the external oblique’s at the edges, and therefore the altissimo Dorsi muscles within the back. The major organs of the abdomen embrace the tiny gut, gut, and abdomen. Together, these 3 flip nutrients into usable energy, moreover as facilitate get rid of solid waste.
Major organs that facilitate filter contaminants out of the body also are within the abdominal region. These embrace the liver and kidneys. The liver is found within the higher right-hand a part of the cavum, underneath the ribs. Though it’s several functions, the liver is best notable for process blood, separating waste from nutrients. The muscles of the abdomen defend very important organs beneath and supply structure for the spine. These muscles facilitate the body to bend at the waist.
The major muscles of the abdomen embrace the muscles abdominals ahead, the external oblique’s at the edges, and therefore the altissimo Dorsi muscles within the back. The major organs of the abdomen embrace the tiny gut, gut, and abdomen. Together, these 3 flip nutrients into usable energy, moreover as facilitate get rid of solid waste. Major organs that facilitate filter contaminants out of the body also are within the abdominal region.
These embrace the liver and kidneys. The liver is found within the higher right-hand a part of the cavum, underneath the ribs.
Though it’s several functions, the liver is best notable for process blood, separating waste from nutrients. The vesicant may be a small sack underneath the liver that holds further digestive juice created by the liver till it’s tense into the tiny gut. Digestive juice helps break down fat. The duct gland is one more gland that produces enzymes to assist your body digest proteins, carbohydrates, and fats.
It conjointly makes hormones that facilitate regulate the distribution of nutrients, together with sugar. Most people have 2 kidneys that are set close to the rear of the body, underneath the ribs, on all sides of the spine. Kidneys filter waste out of the blood that is passed out of the body as excreta. The kidneys conjointly facilitate regulate levels of electrolytes, like salt and metallic element, and manufacture bound hormones that play numerous roles throughout the body.
Because of the necessary organs placed within the abdominal space, several health issues stem from this space. Some include:
Organic process issues within the abdomen or intestines
• Biological process ulcers
• numerous cancers
• Force or strained abdominal muscles
• Cirrhosis of the liver of the liver
• Carcinoma
-
Human cavum
the abdomen is the largest cavity within the body. It’s oval, the extremities of the oval being directed upward and downward. The higher extremity is made through the diaphragm that extends as a dome over the abdomen, just so the hollow space extends high into the bony thorax, achieving on the proper facet, within the exocrine gland line, to the higher border of the fifth rib; on the left facet, it falls below this level by concerning two.5 cm.
- The lower extremity is made by the structures that dress the inner surface of the bony pelvis, mainly the Elevator cuckoo and Coccyges on either facet. These muscles have typically termed the diaphragm of the pelvis. The cavity is wider on top than below and measures additional within the vertical than in the crosswise diameter. To facilitate description, it’s unnaturally divided into 2 halves: A higher and bigger part, the abdomen proper; and lower and smaller half, the pelvis. These 2 cavities don’t seem to be separated from one another; however, the limit between them is marked by the superior aperture of the lesser pelvis.
-
Abdominal cavity anatomy
6.0 Structure of the cavity within the Pelvis
Due to the presence of various girdle organs, the cavity differs in structure between the sexes. The first distinction in structure is that the location of the foremost distal portion of the cavity.
When humans stand or sit upright, any superfluous fluid (which can be blood, pus, or infected fluid) is probably going to gather within the most inferior portion of the cavity. Thus, it’s clinically necessary to remember the variations between males and females.
6.1Male
In males, the rectovesical pouch may be a double folding of serosa set between the body part and therefore the bladder. The cavity is enclosed by males.
How many areas of notes in the feamale?
In females, there are 2 areas of note:
Recto uterine pouch (of Douglas) – double folding of the serosa between the body part and therefore the posterior wall of the female internal reproductive organ.
• Vesicouterine pouch – double folding of serosa between the anterior surface of the female internal reproductive organ and therefore the bladder.
How much cavity enclosed females internal reproductive organs?
The cavity isn’t fully enclosed females – the female internal reproductive organ tubes open into the peritoneal cavity, providing a possible pathway between the feminine reproductive organ tract and therefore the cavum. Clinically, this implies that infections of the duct, uterus, or female internal reproductive organ tubes might end in infection and inflammation of the serosa (peritonitis).
The abdomen (commonly referred to as the belly) is that the body house between the thorax (chest) and pelvis. The diaphragm forms the side of the abdomen. At the extent of the girdle bones, the abdomen ends and therefore the pelvis begin.
Which things are contained by abdomen itself?
The abdomen contains all the organic process organs, together with the abdomen, little and enormous intestines, pancreas, liver, and vesicant. These organs are controlled along loosely by connecting tissues (mesentery) that permit them to expand and to slip against one another. The abdomen conjointly contains the kidneys and spleen.
Many necessary blood vessels travel through the abdomen, together with the arterial blood vessel, inferior venous blood vessel, and dozens of their smaller branches. Within the front, the abdomen is protected by a skinny, powerful layer of tissue referred to as facial. Ahead of the facial are the abdominal muscles and skin. Within the rear of the abdomen are the rear muscles and spine.