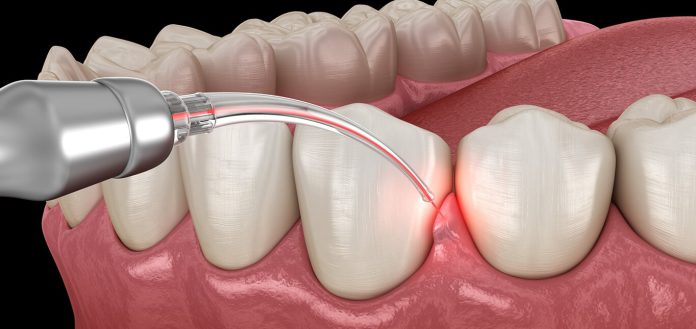
In modern dentistry, technology continues to revolutionize oral health care. One such advancement stands out: laser dentistry’s revolutionary capabilities of precision, versatility and patient comfort – offering patients’ treatment without hassle or discomfort.
Laser dentistry has grown exponentially and now forms an essential element of modern dental practice. Here we will review its many facets, covering its principles, applications, advantages, and challenges in depth.
As we embark on this voyage, we will examine various kinds of lasers used, their specific uses in soft and hard tissue procedures, notable advantages they confer and safety protocols to ensure responsible usage.
Furthermore, we will review the challenges and limitations presented by laser dentistry, offering an in-depth knowledge of its current state and potential prospects.
By exploring case studies and success stories extensively, this review seeks to offer a holistic view of laser dentistry and assist you in selecting the best laser dentistry in Houston and get top-notch dental work.
Table of Contents
1. Introduction to Laser Dentistry
Laser dentistry is an innovative field at the interface between technology and oral healthcare, using laser light for precision dental procedures.
Laser technology dates back to 1960 when the first ruby laser was developed; since then there have been various varieties developed specifically tailored for dental use; today lasers are an integral component of modern dental practices as they offer more minimally invasive approaches than traditional practices.
2. Diode Lasers in Dentistry
Diode lasers emitting wavelengths between 810-980nm are widely utilized for soft tissue procedures as they have the power to reshape gums, treat lesions in oral tissues and promote hemostasis.
Erbium Lasers
Erbium lasers offer wavelengths between 2,700-3, 000 nanometers (nm), making them versatile tools capable of treating both hard and soft tissues alike. Erbium lasers’ pinpoint precision makes them perfect tools for applications including cavity preparation, enamel ablation procedures, surgical operations and many others.
Carbon Dioxide Lasers
Emitting at 10,600nm wavelength, carbon dioxide lasers are frequently employed for soft tissue surgeries such as gingival surgery or tongue tie release.
Absorbent by water molecules makes them effective at cutting through tissues while simultaneously vaporizing them efficiently – applications include gingival and tongue tie release procedures.
3. Advantages of Laser Dentistry
Reducing Pain and Discomfort for Patients
Thanks to laser dentistry’s precise nature and ability to seal nerve endings quickly, laser dentistry helps alleviate both discomfort and pain for its patients while in some instances even eliminating traditional anesthesia altogether.
Minimized Bleeding
Lasers offer great advantages during dental procedures as their coagulative properties help minimize bleeding during procedures, leading to improved visibility for dentists as well as providing patients with more pleasant postoperative experiences.
Precision and Accuracy
Lasers provide highly controlled tissue removal with minimum damage to surrounding areas – ideal for delicate procedures like gum contouring or root canal treatments. This precision can especially beneficial when treating delicate conditions like gingiva.
Faster Healing
Laser procedures offer noninvasive solutions that promote faster recovery times compared to more invasive approaches such as traditional methods. Less trauma to tissues means reduced inflammation and quicker recover times as compared to traditional procedures.
Reduced Anesthesia
Under certain conditions, local anesthetic may be reduced or eliminated altogether to enhance patient experiences – particularly beneficial to those suffering from needle phobia or allergies to traditional anesthetics.
4. Common Applications of Laser Dentistry in Soft Tissue Surgeries
Laser dentistry has become widely utilized for soft tissue procedures such as Gingivectomy for reshaping gums, frenectomies to release oral tissue restrictions, and lesion removal with minimal bleeding and discomfort.
Hard Tissue Procedures
Erbium lasers’ affinity for water absorption allows them to provide precise cavity preparation while protecting surrounding healthy tooth structure from damage.
Periodontal Treatments
Lasers provide an efficient means for periodontal procedures, providing minimally invasive ways of extracting infected tissue, decontaminating root surfaces and stimulating tissue regeneration.
Laser Teeth Whitening
Laser-assisted teeth whitening procedures harness laser energy to enhance bleaching agents for quicker, more effective whitening outcomes.
5. Safety and Guidelines
Adherence to safety protocols is of utmost importance for laser dentistry to minimize any associated risks, so practitioners must abide by established protocols while wearing appropriate protective gear, such as laser eyewear.
Dental professionals receive special training to understand the fundamental principles and characteristics of laser physics as well as safe operating practices for various laser types.
Maintenance and calibration protocols for laser devices have been put in place to ensure optimal performance while also avoiding equipment malfunctions that might endanger safety.
6. Challenges and Limitations of Laser Dentistry
Cost Considerations
While laser dentistry provides many advantages, initial investments for purchasing the device as well as ongoing expenses related to maintenance and calibration can be substantial.
Limited Scientific Evidence
As with any technology, laser dentistry requires further study before being widely accepted and implemented across healthcare practices. Additional research should also be performed in order to develop clear protocols and establish clear guidelines regarding certain procedures.
Contraindications
Specific restrictions regarding laser therapy must be considered before prescribing it to ensure patient safety, such as its use in individuals suffering from certain medical conditions or those taking photosensitive medicines.
7. Patient Experiences
Testimonials about laser dentistry consistently point towards its positive experiences for its users. With minimal pain during and post procedures, minimal bleeding, and faster healing rates all adding up to increased patient satisfaction levels.
Comparative studies between laser and traditional dental methods emphasize their superior comfort and convenience for patients receiving laser dentistry treatments.
8. Introduction into Dental Practice
Integrating laser technology into dental practices requires comprehensive training programs for dental professionals. This involves theoretical knowledge about laser physics, hands-on experience training sessions and ongoing education to stay abreast of advancements.
Undertaking laser treatments requires an in-depth knowledge of their capabilities and limitations in order to select procedures judiciously for maximum patient benefit.
9. Current Trends and Future Prospects
Extant research efforts focus on expanding laser technology’s use within dentistry. Current trends involve the integration of lasers with other technologies like 3D imaging or robotics in order to increase precision and broaden scope of laser assisted procedures.
Future prospects of laser dental technology development include more compact and cost-efficient devices that make its benefits accessible to more dental practices.
10. Case Studies and Success Stories
Real-world case studies showcase the efficacy of laser dentistry across various applications while success stories showcase positive outcomes which highlight its practical advantages in various dental scenarios.
Patient narratives offer invaluable insight into the personal experiences of individuals who have undergone laser-assisted dental procedures, furthering our knowledge about its advantages.
Conclusion
Laser dentistry stands as one of the cornerstones of dental innovation, representing an innovative approach to oral healthcare. Over time this technology has advanced from its infancy into becoming an indispensable asset within modern practices.
Laser dentistry’s array of laser types–diode, erbium and carbon dioxide lasers–demonstrates its versatility; from diodes and erbium lasers to carbon dioxide lasers and more — allows for targeted treatments across a range of dental procedures.
Laser dentistry represents more than technological progress; it represents an evolution in how dental care is delivered and administered, from traditional approaches to innovative practices where precision, efficiency and patient comfort come together seamlessly.
As laser dentistry evolves, its impact will become even more profound on oral healthcare – creating a future in which innovation and personalized patient-centric care come first in dental practices worldwide.